Types of Tube Sheet?


What is Tube Sheet?
A tube sheet is a precision-engineered metal plate that supports and secures tubes within equipment such as heat exchangers, condensers, or pressure vessels. It provides structural stability, maintains precise tube alignment and ensures leak-tight separation between fluid zones.
Each tube hole is drilled and finished to micron-level accuracy to achieve uniform pitch, spacing and sealing integrity. The overall performance and service life of the system depend on the dimensional precision, surface finish and metallurgical quality of the tube sheet.
Tube sheets are produced from various materials including carbon steel, stainless steel, copper-nickel alloys and high-nickel superalloys chosen according to operating temperature, pressure and corrosion exposure. In highly corrosive or aggressive environments, cladded or bimetallic tube sheets are preferred to enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining structural strength.
Types of Tube Sheet
Tube sheets can be classified based on their design configuration, material composition, layout pattern and specific application. Each classification addresses unique engineering requirements such as thermal expansion, corrosion resistance, cleaning accessibility and pressure management. The selection of the right type ensures mechanical stability, leak-tight performance and extended equipment life.
Types of Tube Sheet by Design
- Fixed Tube Sheet: The fixed tube sheet design features both sheets permanently attached to the shell, creating a rigid structure. It is the simplest and most economical configuration, suited for clean-service applications where the shell side does not require mechanical cleaning. When large temperature differences exist between fluids, an expansion joint or bellow is used to relieve thermal stress.
- Floating Tube Sheet: In this arrangement, one tube sheet is fixed while the other is free to move or “float,” allowing the tube bundle to expand and contract independently. This prevents stress accumulation and makes maintenance easier, as the entire bundle can be removed for inspection. Floating designs are preferred in chemical, refinery and power systems that experience wide temperature variations or require periodic cleaning.
- U-Tube Bundle: The U-tube configuration uses a single tube sheet where tubes are bent into a U-shape. This self-compensating design eliminates the need for an expansion joint while providing excellent thermal flexibility. However, internal cleaning of the bent section is limited. U-tube exchangers are used in high-temperature and high-pressure services with the tube sheet always round for even stress distribution.
- Double Tube Sheet: This critical design includes two parallel tube sheets separated by a narrow leak-detection gap. It ensures complete isolation of shell-side and tube-side fluids, preventing cross-contamination. Double tube sheets are essential in pharmaceutical, nuclear and food-grade processes, where product purity is paramount. They are typically round to maintain precise sealing and uniform loading.
Types of Tube Sheet by Material
| Material Type | Technical Overview | Applications & Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (CS) | High-strength, cost-efficient base metal for clean services. | Used in non-corrosive exchangers, ideal for rigidity and economy. |
| Cladded (CS + SS / Cu-Ni) | Dual-metal bonded for strength and corrosion resistance. | Seawater and chemical units, resists pitting and galvanic attack. |
| Stainless Steel (304L / 316L / Duplex) | Weldable, corrosion-proof alloys with hygienic surface finish. | Pharma, food and process plants, long life under thermal cycling. |
| Copper & Cu-Ni Alloys (70/30 | (90/10) | Excellent thermal conductivity and biofouling resistance. |
| High-Nickel Alloys (Inconel / Hastelloy) | High-temperature, oxidation- and chloride-resistant matrix. | Refineries, nuclear and chemical reactors, unmatched durability. |
Types of Tube Sheet by Layout Pattern
Tube sheets can also be classified by the arrangement of tube holes known as the tube layout or pitch pattern. This determines how effectively heat is transferred, how fluid flows around the tubes and how easily the tubes can be cleaned.
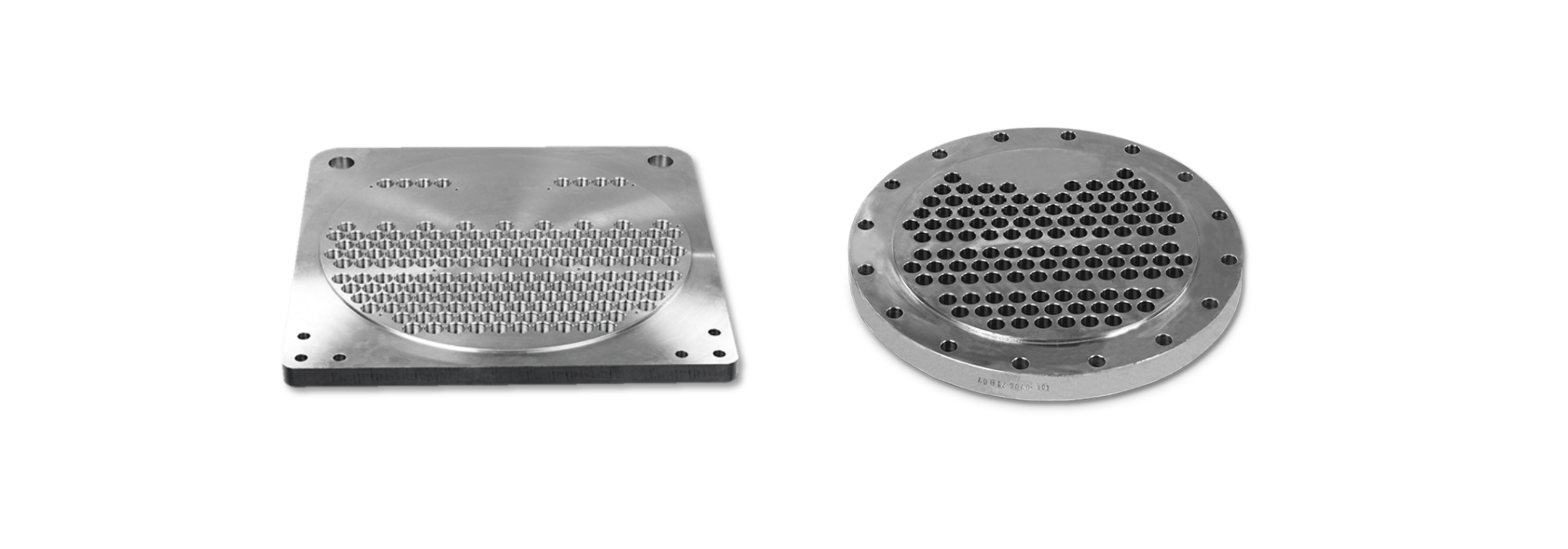

- Triangular Pitch (30° / 60° Layout): The triangular or staggered pitch allows the highest tube density, maximizing heat-transfer area. However, it restricts cleaning access, making it suitable only for clean fluid services.
- Square Pitch (90° Layout): In this pattern, tubes are aligned in a square grid. The open spacing enables mechanical cleaning and lower pressure drop, ideal for fouling or viscous fluids.
- Rotated Square (45° Layout): A rotated square pattern offers a balance between thermal efficiency and cleaning accessibility. It provides better shell-side flow distribution and is used in moderate-duty operations.
- Custom or Mixed Layouts: Some combine multiple layouts such as a triangular core for compactness and a square outer section for cleanability to optimize performance and maintenance.
These layout patterns are widely implemented in fabricated components for shell-and-tube heat exchangers to achieve precise flow distribution and efficient heat transfer.
Applications of Tube Sheets in Heat Exchangers and Process Industries
Tube sheets form the structural base of shell-and-tube heat exchangers, condensers and pressure vessels, maintaining precise tube alignment and ensuring leak-tight separation between fluids. Their reliability directly affects thermal efficiency, pressure containment and overall equipment life. Tube sheets are selected and manufactured according to process temperature, pressure and fluid characteristics, ensuring compatibility with each operating environment. The following sectors represent the most common industrial applications:
- Power Generation: Used in steam condensers, boiler feed-water heaters and turbine lube-oil coolers where constant pressure resistance and thermal stability are essential. Tube sheets in this sector comply with ASME Section VIII and TEMA standards to handle cyclic thermal loads.
- Oil & Gas / Petrochemical: Applied in reboilers, gas condensers and fractionator exchangers. Tube sheets are often cladded or bimetallic, combining carbon-steel strength with corrosion-resistant alloys such as Inconel, Cu-Ni, or Hastelloy to withstand chlorides, hydrogen sulphide and hydrocarbon exposure.
- Chemical and Process Plants: Installed in evaporators, coolers and reactors that handle acidic or alkaline fluids. Materials such as stainless steel 316L, duplex, or cladded carbon steel ensure corrosion resistance and dimensional stability in harsh chemical conditions.
- HVAC and Refrigeration Systems: Used in condensers, evaporators and industrial chillers. Round and square tube sheets support compact layouts and maintain fine surface finishes (up to 0.8 Ra) for efficient sealing and heat transfer.
- Marine and Offshore Applications: Critical components in seawater desalination, ballast-water and engine-cooling systems. Copper-nickel or titanium tube sheets offer biofouling resistance and long-term corrosion protection in saline environments.
- Pharmaceutical and Food Processing: Employed in sanitary heat exchangers where double tube sheets prevent cross-contamination between product and utility fluids. Surfaces are machined to hygienic standards for easy cleaning and validation.
- Renewable and Energy Systems: Used in geothermal condensers, biomass digesters and waste-heat recovery units requiring high-temperature endurance and extended service life.
Why Choose Schilthorn Precision for Your Tube Sheet Requirements?
Schilthorn Precision Engineering manufactures ASME- and TEMA-compliant tube sheets with high dimensional accuracy and consistent machining quality. Using advanced multi-axis CNC and VMC systems, each tube sheet is produced to maintain ±100 µm hole tolerance and fine surface finish up to 0.8 Ra. Materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, copper-nickel and high-nickel alloys, meeting diverse industrial needs from power and chemical plants to marine and HVAC systems. Every component undergoes CMM inspection and process verification to ensure uniformity, corrosion resistance and long service reliability.
